

With the help of Murray loop test, we can easily locate the earth fault and short circuit fault in the underground cable. At first, we describe how does locate earth fault in underground cable:
In this test, the sound cable is used to connect in between test end and far end of the faulty conductor.
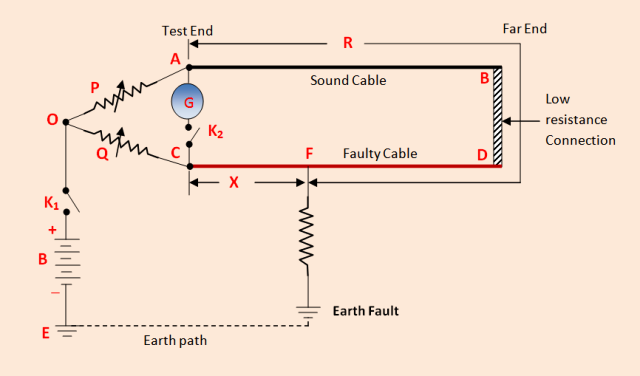
Lets, AB is sound cable, CD is faulty cable, The Earth fault occurs a point F Far end D point of the faulty cable is connected to far end sound cable point B through a low resistance. Two variable resistance ( i.e P. Q ) is connected to the end A point of sound cable and C point of faulty cable respectively.
A battery is connected to point O and Earth point E through a switch K1. And a galvanometer G is connected in between point A and C through a switch K2.
Let, R = Resistance of the conductor loop upto fault point F from the test end point A, i.e resistance of portion AF. X= Resistance in between two points C and F. note that, P, Q,R and X are the four arms of the Wheatstone bridge.
Now, the switch K1 and K2 are closed respectively. Then the variable resistance P & Q are varied till the galvanometer shows zero deflection. In the balance position of the bridge, we get
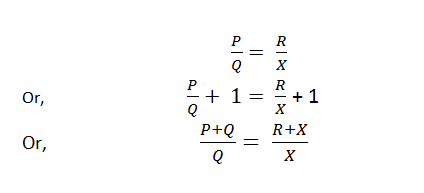
If r is the resistance of each cable, then R + X = 2r
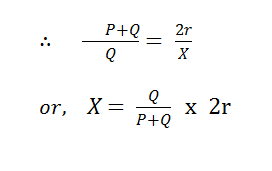
Let, total length of the cable is l meter, so the resistance per meter will be = r/l, Therefore , we can easily measure the fault point from the faulty point is
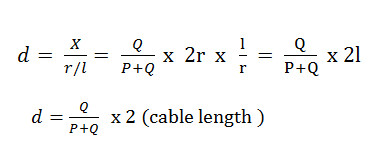
Note that the fault resistance Rf is not in the bridge circuit. So, the fault resistance does not affect the balancing of the bridge. But, if the fault resistance is high, the sensitivity of the bridge is reduced.
It is the same procedure as earth fault test. For short circuit test, battery terminal is connected to the point O and the other point is connected to another faulty cable.
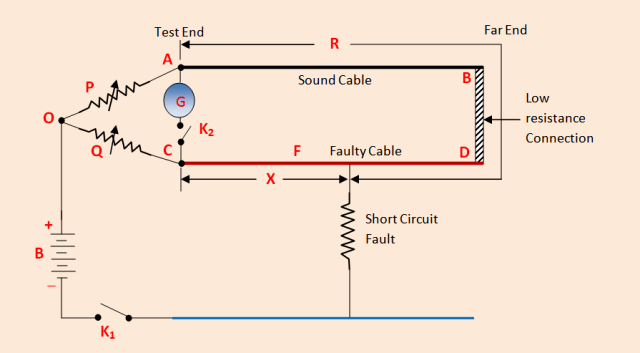
Let, R = Resistance of the conductor loop upto fault point F from the test end point A, i.e resistance of portion AF. X= Resistance in between two points Cand F.
note that , P,Q,R and X are the four arms of the Wheatstone bridge. Now, the switch K1 and K2 are closed respectively. Then the variable resistance P & Q are varied till the galvanometer shows zero deflection. In the balance position of the bridge, we get
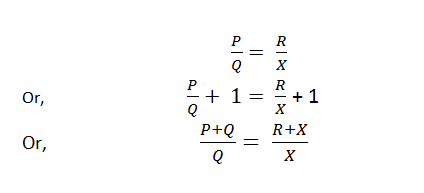
If r is the resistance of each cable, then R + X = 2r
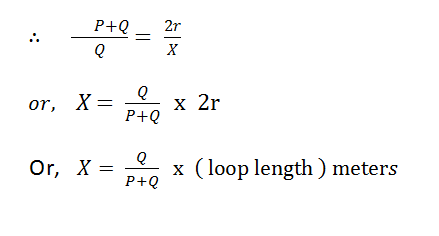
Putting the value of resistance and loop length of the cable, we can easily calculate the fault location.